Multichannel Order Management Methods, Systems, & Tips
Multichannel selling is an effective strategy for maximising sales and diversifying your customer base. But it often comes with unique and challenging logistics requirements: all your inventory, sales, and purchasing data need to be in alignment. If they’re not, you risk disappointing customers and losing revenue.
The solution is to implement a multichannel order management strategy. We’ll cover what that looks like in this guide, along with all the best practices and methods for maximising multichannel success.
Table of Contents
- What is multichannel order management?
- Multichannel vs omnichannel order management
- Challenges of multichannel order management
- Benefits of multichannel order management
- Multichannel order management strategies and methods
- Multichannel strategies for different business models
- What a multichannel strategy means for your supply chain
- What is a multichannel order management software?
What is multichannel order management?
Multichannel order management is the process of integrating order fulfilment, inventory management, and reporting across a company’s various sales channels to create a single source of information. It benefits any business selling products in more than one place – for example, a retailer that operates both a brick-and-mortar store and an online store.
Without an effective multichannel order management strategy, you run the risk of not knowing what’s in stock, what’s been ordered, and what needs replenishing. This can lead to overselling and overstocking, both of which can hurt your ability to conduct business and your reputation.
Additionally, efficient order fulfilment and stock control are essential for effectively selling goods through multiple sales channels. If your processes are too slow, inaccurate, or laborious you’ll feel it in your profit margins.
Multichannel vs omnichannel order management

Multichannel and omnichannel order management are similar but not identical concepts.
Both strategies involve aligning sales, inventory, and reporting across several sales channels. However, omnichannel order management takes it a step further by focusing on creating an integrated and cohesive experience based on the needs and habits of customers.
Challenges of multichannel order management
Unfortunately, the more complex a business becomes the harder it gets to achieve total visibility in all your key areas. Your data can get messy – fast – as sales start flooding in from different online marketplaces, retail centres, and social channels.
The main challenges of multichannel order management you should be aware of are:
-
Implementation cost: To adopt a multichannel order management approach, you’ll likely need to invest in new technology, more staff, and additional operational costs.
- Maintenance cost: The investments above often come with hidden costs that can impact your bottom line, such as maintenance fees, equipment repairs, and hiring costs.
- Increased complexity: Every sales channel has different rules, requirements, and expectations. You’ll need to manage all of these in addition to the potential increase in orders while continuing to provide a satisfactory customer experience.
- Training and change management: Every new tool and process is a new training requirement for staff. Additionally, you’ll need to develop a system for onboarding employees to any new ways of working.
- Inventory management: As orders are fulfilled for sales from different channels, inventory levels will need to be updated across the business to ensure your ‘in-stock’ and ‘out-of-stock’ tags are correct.
- Cross-channel reporting: To properly understand how your business is doing, your multichannel order data needs to be synchronised, so you have a holistic view of key sales performance metrics.
These challenges can feel overwhelming when you first enter the world of multichannel retail. But with an effective multichannel order management system in place, you can simplify and streamline your key processes to mitigate the biggest risks and overcome any pressing obstacles.
Benefits of multichannel order management
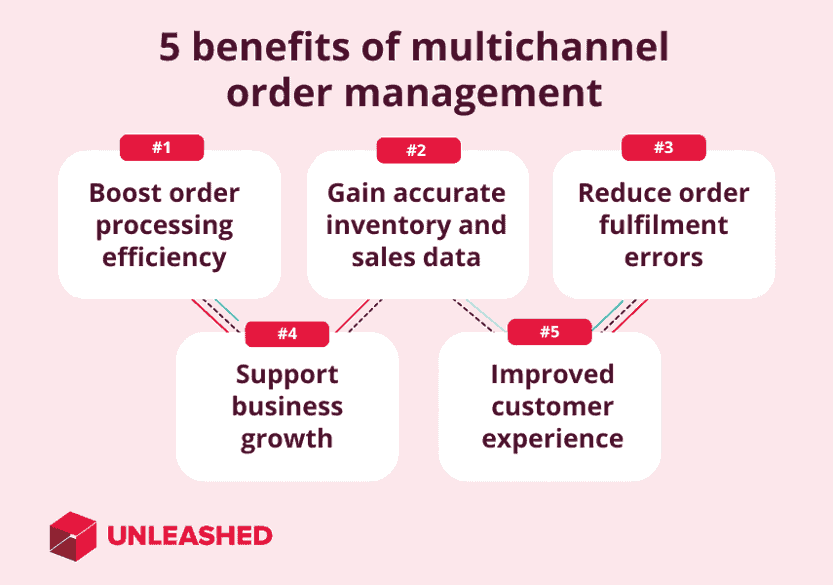
An optimised multichannel order management strategy will help you mitigate business risk, reduce your cost of sales, and gain invaluable visibility across your entire business.
The main advantages of multichannel order management include:
- More efficient processes: Combining systems into a centralised multichannel database allows you to automate, integrate, and streamline your most important workflows.
- Accurate inventory data: Multichannel order management updates inventory levels in real time to help you accurately track stock, replenish at the right time, and protect your cash flow.
- Fewer order errors: Connecting your different channels under one (digital) roof means you’re less likely to oversell or overorder products or make mistakes when fulfilling customer orders.
- Better scalability: Manual systems are difficult to scale because there are only so many hours in the day. Centralised, automated multichannel order management systems are designed to scale alongside your business.
- Improved customer service: By reducing errors, improving communication with customers, and offering more choices, you can improve satisfaction rates and customer loyalty.
To get the most out of your order management system, it pays to have a clear understanding of your company’s needs and the software features most effective at providing solutions for those needs.
Multichannel order management strategies and methods
A multichannel order management (MCOM) strategy is the plan you put in place that defines how you’re going to implement and execute sales through multiple channels, why you’re taking that approach, and any individual steps that need to happen for it to succeed.
It should cover not just the technology you intend to use, but also any processes that will need to evolve, training requirements, IT requirements, and communications with customers.
Here are some methods for developing a successful multichannel order management strategy.
Start with your customers
Efficient order management is for the benefit of your customers, not just your business. You need to understand who they are, where they prefer to shop, and which products interest them most.
Let your customers decide which sales channels you engage with. This will be easier than making them come to you and should improve your brand’s image in the eyes of the consumer.
Establish clear goals
You should have a clear answer to why you’re implementing a multichannel order management strategy. Decide on your priority business goals and objectives. This will then inform the order management performance metrics you need to track, and where you spend your budget.
Consolidate and standardise your inventory
To maximise efficiency and reduce the risk of errors, centralise your inventory data.
As it is often one of a business’s most valuable assets, inventory needs to be accurately and effectively managed. Done poorly, inadequate stock control can lead to cash flow challenges, stockouts, and revenue loss.
Here are some quick best practices for managing your multichannel inventory:
Implement cloud-based software that provides real-time inventory visibility and tracking.
Reconsider your existing inventory management strategy – does it need revising to keep up with multichannel sales? Investigate other tactics for managing goods such as safety stock, Just in Time stock control, and inventory costing methods.
Leverage your sales data to forecast demand and future stock requirements. Compare historical sales data with your own industry expertise and market trends to determine optimal stock levels and reorder processes.
Learn more: What is Multichannel Inventory Management Software?
Integrate your core business processes
For multichannel integration to go smoothly, you need seamless connections between each arm of your business – including inventory management, order processing, CRM, POS, and financials. Look for cloud software applications that offer clean integrations.
This ensures all your business data is up-to-date and accurate everywhere, and your staff can all access the same information, in real time, and share data between platforms.
Don’t forget returns management
Your returns process is a vital component of the customer experience. How you manage customer returns directly impacts how your brand will be perceived in the market. Returns management is the process that governs how to evaluate, process, and communicate about rejected customer orders.
Establish a uniform workflow for dealing with returns from your various sales channels, and prioritise customer satisfaction above all else.
Establish a cycle of continuous improvement
Upgrading your order management system shouldn’t be a one-and-done project. Technology will always change, along with the expectations of customers. To prepare for these changes you must implement a system for reviewing and revising your multichannel strategy.
Measure the performance of your order management system and use this data - in conjunction with external learnings - to regularly adjust and improve your ways of working.
Multichannel strategies for different business models
Multichannel order management (MCOM) strategies vary significantly depending on the business model. Each model has distinct operational requirements, pricing structures, and customer expectations. Understanding these differences is critical for designing an effective MCOM system that supports seamless transactions across all channels – let’s explore the key requirements for different business models:
Multichannel Strategy for B2B
Key Requirements:
- Complex Pricing Structures: B2B transactions often involve tiered pricing, negotiated discounts, and contract-based rates. Your MCOM system must support dynamic pricing rules and customer-specific agreements.
- Bulk Orders: Unlike retail, B2B orders typically involve large quantities. The system should handle volume-based pricing, palletized shipping, and inventory allocation for high-volume transactions.
- Approval Flows: Multi-level approval processes are common in B2B procurement. MCOM platforms need to integrate with ERP or procurement systems to manage purchase authorizations, credit checks, and compliance workflows.
- Integration Needs: Seamless connectivity with CRM, finance, and supply chain systems ensures accurate invoicing and real-time inventory visibility for large-scale operations.
Multichannel Strategy for B2C
Key Requirements:
- Transparent Pricing: B2C customers expect clear, consistent pricing across all channels. Promotional pricing, discounts, and loyalty programs should sync in real time.
- Order Flexibility: B2C orders are smaller but frequent, requiring fast processing and multiple delivery options such as home delivery, BOPIS (Buy Online, Pick Up In Store), and same-day shipping.
- Customer Experience: The focus is on convenience and personalization. MCOM systems should provide real-time stock visibility, accurate delivery estimates, and integrated returns management.
- Scalability: High transaction volumes during peak seasons demand robust systems capable of handling spikes without compromising performance.
Multichannel Strategy for D2C
Key Requirements:
- Direct Engagement: D2C brands prioritize customer relationships. MCOM systems should integrate marketing automation, subscription models, and personalized offers.
- Dynamic Pricing & Promotions: Frequent flash sales, influencer-driven campaigns, and bundled offers require agile pricing capabilities.
- Inventory Synchronization: Real-time inventory updates across eCommerce platforms and social selling channels are essential to avoid overselling.
- Streamlined Fulfillment: D2C strategies often leverage hybrid fulfillment models, including Ship-From-Store and micro-warehousing, to reduce delivery times and costs.
What a multichannel strategy means for your supply chain
Adopting a multichannel strategy has a direct impact on a business’ supply chain and creates different priorities for both retailers and their suppliers.
For retailers, supply chain priorities include increasing on-shelf availability while reducing inventory stock and growing multichannel capability. While for suppliers the priorities are to reduce operating costs while improving service levels, inventory control and forecast accuracy.
Consumers are browsing and buying online more frequently, and with this comes greater expectations regarding their purchase delivery and pick-up options.
As a result, retailers must determine how to create a customer experience that is seamless, irrespective of channel, order size, origin and delivery choice. To address the ongoing changes in consumer behaviour, retailers need to optimise their supply chains around these three key areas:
Order fulfilment
Product distribution is a critical process of the supply chain, and multichannel order fulfilment means retailers need to leverage supply chain operations and processes to fulfil traditional store orders while also competing with individual customer orders online.
To determine an optimal order fulfilment strategy, retailers must ascertain their customers’ expectations of multichannel experiences, then decide how to manage these expectations while managing the costs of carrying inventory stock and transportation costs. To help determine the best delivery method for their business, they must first understand the different types of fulfilment strategies currently available.
- Integrated fulfilment allows retailers to use existing facilities to leverage inventory stock across channels. Inventory stock is then segmented during shipping activity.
- Dedicated fulfilment through independent fulfilment centres develop and categorised inventory stock by selling channel. Tailoring operations within each channel based on specific order profiles, frequencies and the value-added service needs of each channel or customer type.
- Hybrid fulfilment provides a combination of integrated and dedicated fulfilment centres, allowing retailers to create their own models. For example, retailers can have separate inventory stocks for retail replenishment and consumer-direct orders in a single facility.
- Ship-From-Store (SFS) turns physical retail locations into mini-fulfilment centres. This approach optimises inventory usage, reduces delivery times, and lowers shipping costs by fulfilling online orders from the nearest store.
- Buy Online, Pick Up In Store (BOPIS) offers customers the convenience of purchasing online and collecting their orders in-store. This strategy improves customer satisfaction, reduces last-mile delivery costs, and drives additional in-store sales opportunities.
A multichannel service offer should consider special delivery options including speed and timing of delivery and real-time information on order status so that customers can track their purchases from order placement to dispatch and delivery. Fulfilment systems should integrate logistics activities for warehouse operations with smart order routing, ensuring inventory is allocated and delivered to all destinations such as brick-and-mortar stores as well as for the individual online customers.
Returns
Consumers are more likely to make online purchases with businesses that offer an easy and efficient returns policy. Regardless of channel, they expect returns to be processed quickly, to receive an exchange product or to get reimbursed the purchasing price.
They are also increasingly more likely to purchase a product online from a company that offers free returns or the option to return an item to a store.
Therefore, today’s multichannel businesses need to have a robust reverse supply chain. By allowing customers the option of an in-store return or exchange, businesses can avoid the cost and time of returning via other means.
With that in mind, reverse logistics goes beyond simply accepting returns - it involves a structured process to manage returned goods efficiently:
- Initiation: The return process begins when the customer requests a return through an online portal, customer service, or in-store interaction. The system should generate a return authorization and provide clear instructions to the customer.
- Inspection: Once the product is received, it undergoes a quality check to determine its condition. This step decides whether the item can be restocked, repaired, or needs disposal.
- Disposition: Based on inspection results, the product is either returned to inventory, refurbished, recycled, or discarded. Efficient disposition reduces waste and recovers value wherever possible.
By using a multichannel order management (MCOM) system, businesses can simplify what could be a complex returns process from multiple sales channels and physical locations by:
- Capturing Reason for Return (RFR) data at the point of initiation.
- Aggregating and analyzing RFR data to identify patterns and root causes.
- Generating actionable insights that:
- Improve supply chain quality control by addressing recurring defects or packaging issues.
- Enhance product descriptions to reduce mismatched expectations.
- Refine demand forecasting by understanding customer behavior and product performance.
By leveraging these insights, businesses can reduce return rates, improve customer satisfaction, and optimize inventory planning.
Inventory control
Inventory control efficiency is crucial for balancing and managing inventory stock between different locations.
A centralised, real-time multichannel inventory control system will provide transparency across all sales channels eliminating the risk of lost sales due to stockouts.
Based on sales, you can project when stock will run out and make sure you replace it in a timely manner. It also allows you to transfer stock from one channel to another and offers the functionality to provide eCommerce shoppers with access to view inventory stock levels prior to purchase.
Retailers and suppliers who work together to improve products and operations can reduce material costs, improve delivery times and reorder flexibility. Suppliers will be more willing to work with you to solve problems if you have a mutually beneficial relationship. Maintaining a good relationship with product suppliers can make the difference between inventory fails and successful inventory control.
What is a multichannel order management software?
Multichannel order management software is a digital system designed to automate and streamline purchasing, sales order management, shipping, inventory, and pricing across multiple online and offline sales channels. It makes these workflows simpler and more cost-effective by integrating crucial data points into a single, cloud-accessible source of information.
Key multichannel order management system features
Multichannel order management systems come with a variety of features and add-ons suitable for different business sizes, strategies, and budgets. Here are the most crucial features to consider.
Integrated sales channels and point-of-sale (POS) systems
Powerful software integrations are at the heart of multichannel order management.
Your sales channels need to connect seamlessly to your multichannel order manager and POS plug-ins (or physical terminals) to ensure accurate tracking of inventory and sales data. The ideal system will also integrate with other areas of the business – such as finance and CRM – to achieve further efficiency gains and cost savings.
Real-time inventory tracking
Multichannel order management is facilitated by real-time inventory management software functionality. This means your inventory levels are updated across your different sales channels and central platform as changes happen.
Real-time inventory control also enables you to track all the costs associated with each of your products, providing an accurate picture of your margins at the business and product levels.
Centralised order processing
With integrated sales channels and synchronised inventory, you will already have centralised two key elements of order processing. Make sure your system can also identify and track individual customer order statuses and print appropriate shipping labels.
Multiple warehouse support
If you’re selling through multiple channels, there’s a good chance you’re fulfilling orders and holding stock in more than one location. To ensure accuracy across your whole business, you’ll need an order management system that’s capable of tracking stock and sales in multiple warehouses or retail stores.
Process automation
A crucial factor of any software is its ability to make your day-to-day work easier and more efficient. In the case of multichannel order management, that means automating repetitive processes such as purchase order creation, order routing, reporting, and demand forecasting.
Optimise your multichannel sales process with Unleashed

Effective multichannel order management can be hard to achieve. Unleashed helps you streamline the entire process by bringing all your sales channels, inventory data, and purchasing processes under one roof. You can manage your entire business on the cloud while keeping an accurate track of every financial movement as it happens – saving you time and money while protecting your cash flow.
If you’re ready to optimise your multichannel sales process with Unleashed, here are the next steps:
- Watch a software demo. Discover how our cloud-based multichannel software helps you automate key order management processes and connect all your sales channels to boost efficiency and slash operational costs.
- Sign up for a free 14-day trial of Unleashed. Do you prefer a hands-on experience? Jump inside the software and explore the benefits for yourself with a risk-free two-week trial of Unleashed.
- Chat with a multichannel integration expert to assess your needs. Book a free chat with one of our in-house experts for an honest discussion about the multichannel order management solution that’s right for you.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is multichannel order management important for businesses?
It prevents overselling, stockouts, and order errors by synchronizing inventory and sales data across channels. This improves efficiency, reduces costs, and enhances customer satisfaction.
How does multichannel order management improve returns handling?
An MCOM system simplifies reverse logistics by:
- Capturing Reason for Return (RFR) data
- Automating return authorization and inspection workflows
- Generating insights to improve product quality and reduce future returns
How does multichannel order management benefit B2B vs B2C businesses?
-
B2B: Requires complex pricing, bulk order handling, and approval workflows.
-
B2C/D2C: Focuses on fast delivery, transparent pricing, and personalized customer experiences.











